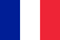
Hemorrhoids are a disease in which blood congestion and abnormal changes occur in the veins of the rectum or around the anus. Such a delicate pathology has no age and gender restrictions.
The underlying factor that leads to the formation of hemorrhoidal cones is stagnation, which in turn results from a variety of other predisposing factors.
The pathology is characterized by characteristic symptoms that a person can not ignore. The most specific clinical signs of hemorrhoids are itching and burning in the anal area, rectal bleeding, and severe pain in the perianal region.
The doctor can make the correct diagnosis based on a physical exam, but some laboratory and instrument tests may also be required.
Treatment of hemorrhoids depends directly on the severity of the course of the disease, which is why it can be done both conservatively and surgically.
Since there are many variants in pathology, it is coded with several meanings in the International Classification of Diseases.
etiology
The main reason for the appearance of hemorrhoidal cones is:
- violation of the function of the vessels of this organ;
- increased arterial blood flow;
- Disruption of the outflow of blood from the venous plexus;
- Loss of tone of the rectal veins, which leads to their expansion and the appearance of nodules.
In addition, clinicians identify a variety of unfavorable factors that lead to the above processes, which is why they are usually divided into several groups - pathological and physiological.
The first category of causes of hemorrhoids includes:
- chronic constipation - hardened feces injure the walls of the rectum and anus;
- severe poisoning of the body - this should include poisoning with alcoholic beverages, toxic and chemical substances, as well as low-quality foods;
- severe diarrhea of an infectious nature;
- the formation of malignant, less often benign, tumors in the intestine;
- Diseases of the pelvic organs such as prostatitis or cystitis;
- inflammatory diseases of the digestive system;
- hormonal disorders;
- portal hypertension and cirrhosis of the liver, as well as other diseases of this organ. The connection of hemorrhoids with the liver is due to the presence of common veins;
- the pathological influence of pathogenic bacteria that lead to the development of infections.
In addition to diseases and disorders, the causes of hemorrhoids may not be related at all to the presence of one disease or another in the body. Among the physiological factors, it is worth highlighting:
- Lack of physical activity - this happens against the background of a variety of sources - laziness, a serious illness that deprives the patient of the ability to move, as well as specific working conditions in which a person is forced to sit or stand most of the working hours;
- excessive body weight;
- poor nutrition - this includes the abuse of fatty, spicy foods, smoked meats, confectionery, carbonated beverages, semi-finished products, fast food, and other harmful ingredients. For this reason, diet therapy is one of the components of hemorrhoid treatment;
- indiscriminate use of medication, including laxatives or oral contraceptives;
- incorrect implementation of proctological diagnostic procedures or enemas;
- unconventional sexual preferences, namely anal sex;
- prolonged influence of stressful situations;
- perform heavy physical activity;
- Practicing certain sports, in particular cycling or motorcycling, equestrian sports and other types of weight lifting;
- excessive drinking and smoking of cigarettes;
- Length of birth of a child or work;
- Menstruation.
Genetic predisposition plays an important role in the development of the disease. Diagnosing a similar pathology in one of the closest relatives significantly increases the likelihood of bumps. Knowing this, you can independently prevent the occurrence of a disease. You just need to follow all the rules for preventing hemorrhoids.
classification
Due to its clinical nature, the disease is:
- acute - this is the first manifestation of hemorrhoids that was previously undiagnosed;
- chronic - characterized by alternating phases of exacerbation of symptoms and their withdrawal.
Depending on the area of hemorrhoid formation, cavernous pathology is divided into:
- external hemorrhoids - is the case when the lump appears under the skin of the anus, and not under the mucous membrane of the rectum. It is considered the rarest form of the disease;
- internal hemorrhoids are the most common type of pathology in which vascular cones appear directly in the anal canal;
- mixed hemorrhoids - the second most common type of disease, which is characterized by the presence of signs of the two forms described above.
In addition, there are types of hemorrhoids, divided according to their severity:
- mild course - symptoms may be completely absent or only slightly pronounced. Conservative methods predominate in therapy;
- moderate - differs in the addition of pain sensations caused by an increase in the nodes and their injury by feces. Internal bumps fall out during bowel movements and adjust afterwards. It is possible to get rid of the disease using minimally invasive methods;
- severe - characterized by the expression of such a sign of hemorrhoids as bleeding. The knots can fall out not only during defecation, but also in all other situations that lead to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. In such cases they can only be adjusted manually. The tactic of getting rid of hemorrhoids can include both minimally invasive procedures and extensive surgery;
- complicated - is expressed by an increase in the symptoms of the disease, and during the diagnosis the development of complications, one of which may be thrombosis, is often observed. It should be noted, however, that premature treatment of hemorrhoids does not always result in consequences.
Symptoms
The first signs of hemorrhoids can be so slight that a person will ignore them. The first clinical manifestations are:
- slight discomfort in the anus;
- not intense itching in the anal area;
- Pain when defecating;
- Swelling of the entrance to the anal canal.
As the disease progresses, the following symptoms of hemorrhoids appear:
- Burning and severe itching;
- increased pain, which occurs not only when defecating, but also when walking intensely or sitting for a long time;
- the appearance of impurities of blood and mucus in the stool. It is noteworthy that pathological clots do not mix with feces, but are located above them;
- prolapse of the hemorrhoidal node, which leads to severe pain;
- Redness of the skin of the perianal region;
- Rectal bleeding - if such a sign of early-stage hemorrhoids could only manifest itself in the form of smear of blood on toilet paper or underwear, then with a complicated course the bleeding can reach the intensity of the beam. This is what often leads a person to seek help.
In addition to specific clinical manifestations, the above symptoms of hemorrhoids can be supplemented with an increase in body temperature, which indicates the progression of the inflammatory process.
diagnosis
It often happens that when symptoms of the disease appear, a person does not know which doctor to turn to for hemorrhoids. A proctologist or surgeon is involved in diagnosing and treating hemorrhoids, but you can contact a therapist for the initial consultation. It should be noted that if a child shows signs, it should be shown to a pediatrician immediately, and if a pregnant woman first consults an obstetrician-gynecologist.
The first stage of diagnosis includes the work of the clinician, which aims to:
- a detailed questioning of the patient for the first time the signs of hemorrhoids appear - to identify the stage of the disease process;
- Familiarity with the medical history and life history not only of the patient, but also of his relatives - often this is enough to determine the sources of the appearance of hemorrhoids;
- Carrying out an objective examination to assess the condition of the perianal region, as well as a digital examination of the rectum, which makes it possible to distinguish internal hemorrhoids from external ones and determine the location of the nodule.
The second step in establishing the correct diagnosis is laboratory tests, namely a general, biochemical blood test and coagulogram.
The last part of the diagnosis is instrumental examinations of the patient, the aim of which is to assess the appearance of hemorrhoids and ensure that:
- Sigmoidoscopy;
- Anoscopy;
- Colonoscopy;
- Radiography using a contrast agent;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
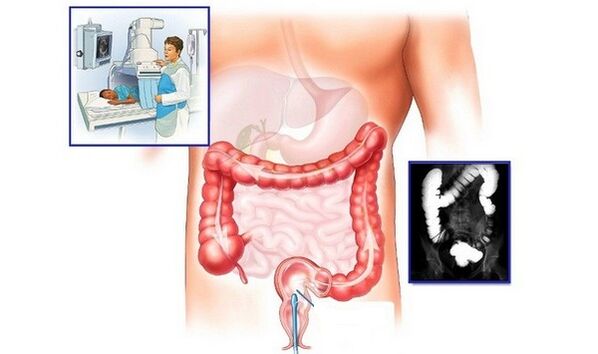
Only after studying the results of the examination does the clinician develop a tactic for curing hemorrhoids in a patient.
treatment
The treatment regimen for the disease depends on the severity of the disease, but common methods of treating hemorrhoids include:
- the use of drugs for both local and general effects. In the first case, rectal suppositories, ointments, creams and gels are used, and in the second - tablets to improve blood circulation, strengthen veins and neutralize accompanying symptoms;
- Adhering to a frugal diet - shown for external and internal hemorrhoids. All recommendations regarding the menu and cooking methods are given by the attending physician;
- minimally invasive techniques for removing hemorrhoids;
- open surgery;
- the use of alternative medical prescriptions. This includes the preparation of candles and ointments from natural ingredients at home, as well as decoctions made from medicinal herbs and plants that are used for ingestion or as microclysters and hip baths.
Among the minimally invasive methods of treating hemorrhoids, it is worth highlighting:
- the introduction of sclerosing substances directly into the node;
- Ligature with latex rings;
- Infrared and electrocoagulation;
- Cryogenic destruction;
- Devaluation.
The tactic for removing hemorrhoids is determined by the stage of the pathology.
If conservative methods are ineffective, as well as if the course of the disease is complicated, open surgical intervention is indicated - hemorrhoidectomy.
Treatment of hemorrhoids in pregnant women and children is recommended by an obstetrician-gynecologist and a pediatrician.
Possible complications
Ignoring pronounced clinical phenomena and treating hemorrhoids late, often leads to the development of the following consequences:
- Joining a secondary infection;
- the spread of the inflammatory process;
- Anal sphincter insufficiency;
- profuse bleeding leading to anemia;
- Proctitis and paraproctitis;
- the formation of blood clots;
- Anal fissures.
Prevention and prognosis
To prevent the occurrence of hemorrhoids, it is necessary to observe the following rules of prevention:
- lead a healthy and moderately active lifestyle;
- eat right and balanced;
- strengthen the pelvic and abdominal muscles;
- only take medication as directed by your doctor;
- Avoid physical and emotional stress whenever possible;
- timely management of constipation and other pathological causes of hemorrhoids;
- Make sure the body weight is within normal limits;
- regularly undergo a full physical exam.
The question of the prognosis of hemorrhoids cannot be answered unequivocally, since the result depends on several factors - the stage and form of the course of the disease, the age category, the time to start hemorrhoid treatment, and the patient's compliance with all the recommendations of the clinicians.
Often times, people diagnosed with hemorrhoids ask if they can go away on their own. Doctors' answer will always be negative - the disease will become chronic.